Properties of Nanomaterials

Presented by


Types of Nanotubes and Their Properties
Types of Nanotubes
- Inherent issue in the synthesis of carbon nanotubes (CNTs):
- 30-40 different types of nanotubes per batch.
- Metallic vs Semiconducting.
- Singled-walled versus multi-walled.
- Different lengths and diameters.
- Very difficult to separate them.
- Need a better process to produce the specific type wanted.



Types of Nanotubes
- Think about a nanotube as a piece of rolled up graphene.
- This isn't how they are made, but an easy way to visualize them.
- Depending on the section “cut out” to roll up, the carbon atoms are going to have different orientations or “twists” across the tube.
- These have been named zig-zag, armchair, or chiral based on the pattern of the carbon rings.


Conductance:
- In general, the “twist” of the nanotube is called the chirality.
- The chirality affects the conductance of the nanotube, it's density, it's lattice structure, and other properties.
- Nanotubes are either metallic or semi-conducting based on their chirality.
Metallic v Semi-conducting


Conductance and Chirality
- Chirality is represented as a vector (n,m).
- Armchair: n=m; (n, n).
- Zig-zag: m=0 (n, 0).
- Chiral: (n, m).
- A SWCNT is considered metallic if the value n - m is divisible by three. Otherwise, the nanotube is semiconducting.



vector: (10,0)
vector: (7,3)
vector: (10,7)
Semi-conducting & zig-zag
Semi-conducting & chiral
Metallic & chiral

Surface-to-Volume Ratio
Where Surface is Important
Many technologies are based on surface interactions, including:
- Filtration.
- Air and water purification.
- Heat transfer.
- Catalysis.
- Sensors technologies.
- Super-batteries.
Very large surfaces for little material are needed!!


Surface to Volume Ratio (S/V)
Definition: Amount of surface area per unit volume of an object
surface area:volume or
surface area
volume

Ex: S/V of a cube (with side a = 1 cm)

Visualize S/V Ratios
- A large cube made up of smaller cubes has a much greater S/V ratio.
- Each tiny cube contributes surface area to the overall area, where the volume remains the same.

Smaller Item, More Surface Atoms
Nanomaterials have a large number of surface atoms and thus a large surface-to-volume ratio.
- The larger the surface-to-volume ratio, the more atoms are located on the surface.
- Surface atoms behave very differently than inner atoms.

Fraction of the atoms on the surface
Carbon-based Nanomaterials
EVERY ATOM IS ON THE SURFACE!

Comparing Materials: Carbon
Compare S/V of carbon nanomaterials to other forms of carbon
For example: Diamond vs Carbon Nanotubes.
- Diamond: C bound to 4 other C's; arranged in a tetrahedral geometry.
- Nanotubes: C bound to 3 other C's; arranged in a tubular shape.
- A diamond has a crystalline unit cell structure throughout the entire material, while nanotubes are 1 carbon atom thick tube-like materials with ALL ATOMS ON THE SURFACE.


Carbon Nanotube
“Dissolved” Nanoparticles
Gravity, Buoyancy, Sinking, Floating
An object will float when placed in a fluid of higher density, it will sink when the fluid has lower density.

Gravity, Density, and Floating
Let’s observe a piece of Styrofoam and a chunk of gold in a glass of water.

LiCl: Floating or Sinking?
Lithium Chloride (LiCl)
Density LiCl = 2.1 g/mL
Li+ = 7 g/mol
Cl- = 35.45 g/mol

Water
Density H2O = 1 g/mL
H2O = 18 g/mol
Solvation
Solvation forces are much stronger than gravity and buoyancy for an ion.

In between
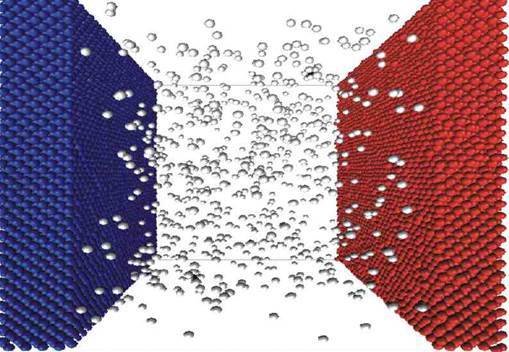
- Nanopartilces behave like larger atoms/ions.
- They do not "feel" gravity.
- They have strong solvation effects.
- Gold nanoparticles act like something in between a chunk of gold and gold ions (Au3+).
- Gold nanoparticles act as a suspension in water, not a solution.


This lesson was presented by:
To learn more about nanotechnology, visit omninano.org

